Definition of Inflation
Inflation means a sustained increase in the aggregate or general price level in an economy. Inflation means there is an increase in the cost of living.
“inflation means that your money won’t buy as much today as you could yesterday. ”
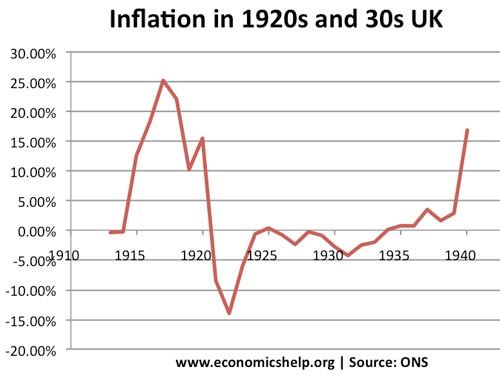
In the UK the rate of inflation has varied a lot from 25% a year in 1974 to the deflation in the 1920s and 1930s.
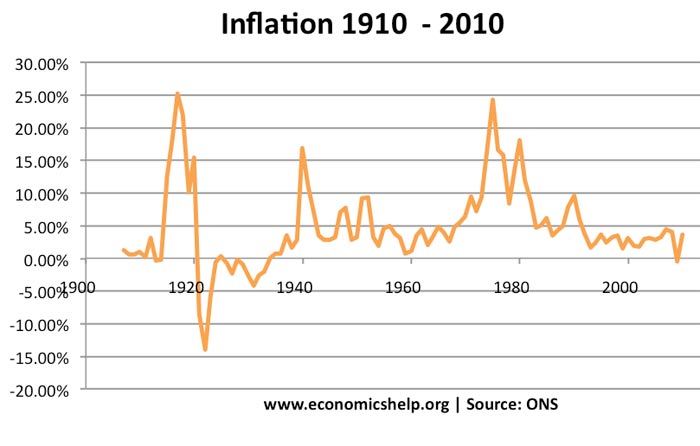
See: Historical Inflation Rates for more details
Note on reading Inflation rates:
- Between August 1974 and August 1978, the rate of inflation feel from 25% to 8%. This means the price level was increasing at a slower rate.
UK Inflation Since 2000
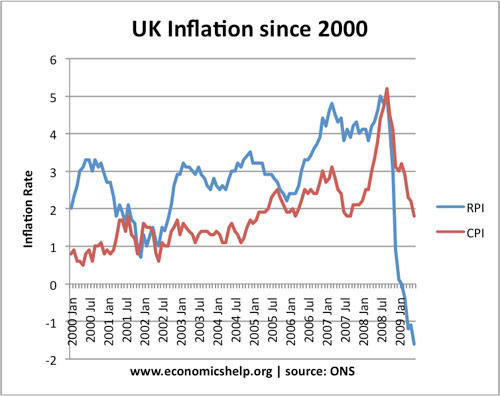
- Inflation was close to the governments target of 2% between 2000-2007
- In 2008, inflation peaked at 5%, primarily because of a surge in the price of oil.
- Inflation fell in 2009, because of the recession and fall in demand.
- RPI measure became negative because it includes mortgage interest payments, and interest rates were cut during this period.
Definition of Deflation
Deflation is a fall in the price level of the economy. It means there will be a negative inflation rate.
CPI and RPI Measures of Inflation
RPI – retail price index includes mortgage interest payments and so tends to be more volatile. A cut in interest rates will reduce RPI
CPI – Consumer Price Index excludes mortgage interest payments
Purchasing Power of Money and Inflation
If we have inflation then £100 is going to buy less in the future
Purchasing power of the pound (1920=100)
1920
|
1930
|
1940
|
1950
|
1960
|
1970
|
1980
|
1990
|
1998
|
100
|
125
|
129
|
98
|
66
|
46
|
133
|
6.8
|
5.33
|
This table shows us that £100 buys less goods in 1998 than 1920, (approx 78% of its value)
- Therefore another definition of inflation is a decline in the purchasing power of money.
The real value of money is the amount of goods it can buy
If you had a fixed income of £100 then the nominal value remains unchanged but the real value has fallen by 95 % in the last 78 years.
If you had a fixed income of £100 then the nominal value remains unchanged but the real value has fallen by 95 % in the last 78 years.
- The rate of change of the price level is known as the rate of inflation e.g. if the price level doubles then the rate of inflation is 100%
- If the rate of inflation falls (e.g. from 10% to 2%), prices are still rising but at a slower rate.
Hyper Inflation
Definition of hyper inflation. This is generally considered to occur when inflation is greater than 1000%. With hyper inflation money loses its value so rapidly that nobody wants to use it as a medium of exchange
In 1920s Germany had inflation of 100 billion %
In 1946 Hungary had inflation of 42,000 billion per cent
In 1946 Hungary had inflation of 42,000 billion per cent

No comments:
Post a Comment